Monitoring background job is important because once you schedule the job it might be canceled due to some error. To investigate the root cause use SM37.
Step 1) Execute T-code SM37.
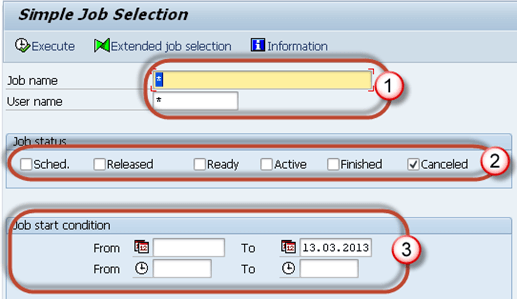
Step 1) Execute T-code SM37.
Step 2) Fill the required criteria.
- Job name and username(who scheduled the job). You can put * to get details of all jobs scheduled by all the users.
- Select job status which you want to monitor. If you find that a background job is not completed, select Canceled status.
- Put the date range as per your requirement.
Step 3) You will get a screen as shown below.
Step 4) Click on Job Log button to trace the error due to which job was canceled.
Step 5) You will get the following details. In the below example, job was canceled since there was an issue with RFC connection to the remote system. As a resolution use SM59 to check if there is an authorization issue to the remote system.
Sometimes jobs in Active status may also cause an issue.
You may face issues like tablespaces are full; the duplicate job is running with the same name and timing, job is selecting or updating large data, etc.
You can also check such jobs from SM37. Follow the procedure as below.
Step 1) Execute SM37.
Step 2) Fill the required criteria.
You can also check such jobs from SM37. Follow the procedure as below.
Step 1) Execute SM37.
Step 2) Fill the required criteria.
- Job name and username(by which job is scheduled).
- Select job status which you want to monitor. If you find a system performance issue or if a task is not completed for a very long time, then select active status.
- Put the date range as per your requirement.
Step 3) Look into Duration column (which signifies the job is running since n seconds). If you find a large number in duration then investigate the job details from job log. Some jobs use a large number of data.Using SE16 check table entries for the tables used by the job.
Sometimes jobs show to be in Active Status even though they are completed.
How to correct them? Follow the below set of procedure -
Step 1) As shown above, Execute T-code SM37 and select the job with an active status.
Step 2) Select the active job which is causing the problem.
Step 1) As shown above, Execute T-code SM37 and select the job with an active status.
Step 2) Select the active job which is causing the problem.
Step 3) Click the Job->Check status.
Step 4) In the status bar of the window you will find as below message. This will repair Job Status if there was a problem
Step 5) If still job is in running status then goto SM50. Below screen will open. Have a look at "Reason" column which shows any errors or exceptional issue. Investigate it further.










No comments:
Post a Comment